Introduction
Imagine having a professional trader whispering in your ear, telling you exactly when to jump into the market and when to get out. That is essentially what a Forex Signal is.
For many traders—especially those balancing a day job or those just starting out—staring at charts for hours isn't feasible. Forex signals bridge that gap. They are "shortcuts" or actionable alerts that provide you with the specific details needed to execute a trade without doing all the heavy lifting of technical analysis yourself.
What Actually Is a Forex Signal?
At its core, a Forex signal is a recommendation to either Buy or Sell a specific currency pair at a specific time and price.
These signals aren't random guesses. They are typically generated in two ways:
-
Human Analysis: Experienced analysts look at support/resistance zones, news events, and chart patterns to find high-probability setups.
-
Automated Algorithms (EAs): Software scans the market 24/7 looking for mathematical criteria to trigger an alert.
Regardless of the source, the goal is the same: to help you profit from market movements with calculated risk.
The Anatomy of a Signal: How to Read It
This is the most critical part. A signal can look like a confusing string of numbers if you don't know the code. Let’s break down a standard signal format you might see on a dashboard, Telegram, or email.
The Example Signal:
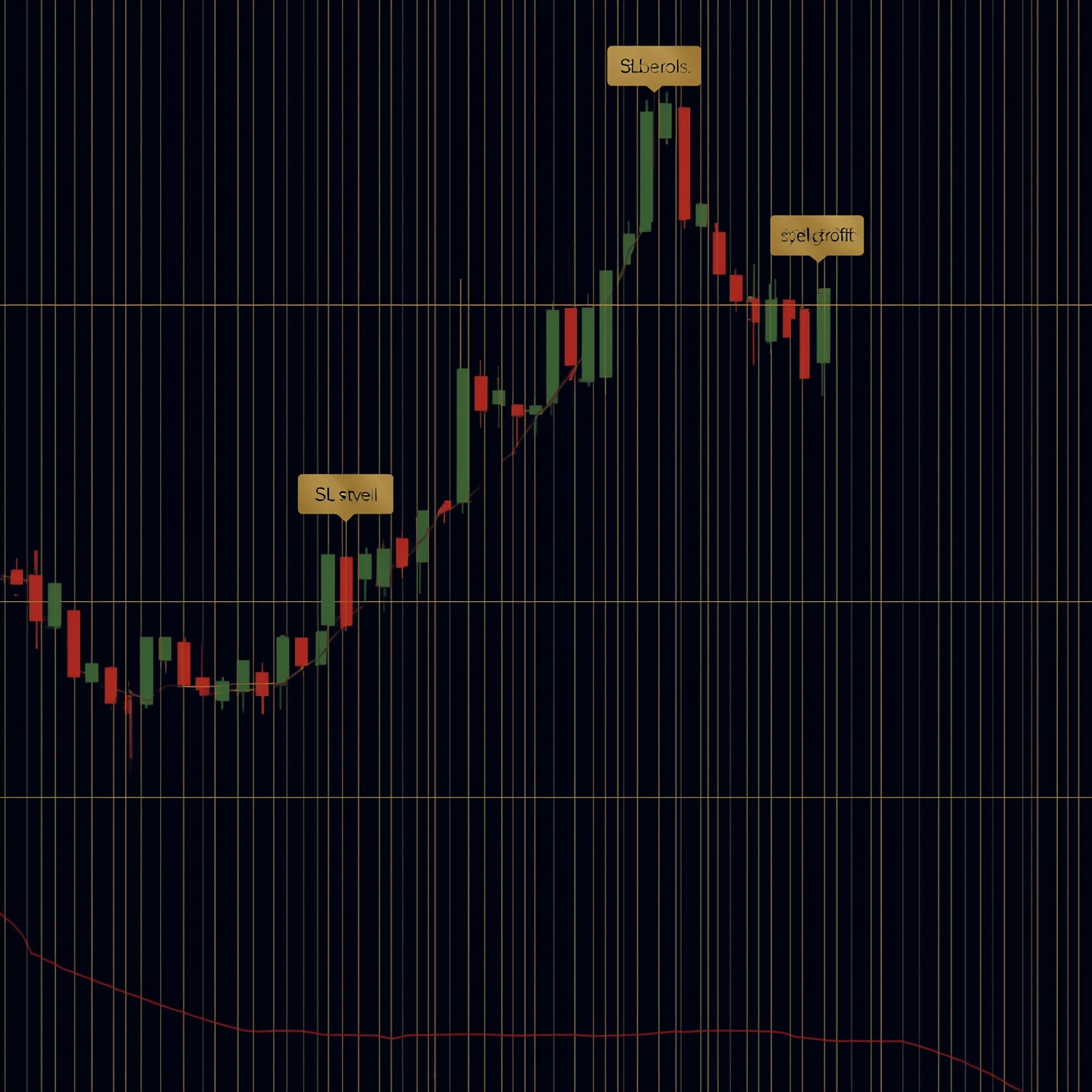
EUR/USD BUY @ 1.0850 SL: 1.0820 TP: 1.0900
Here is how to translate that into action:
1. The Pair (Asset): EUR/USD This tells you what you are trading. In this case, it's the Euro against the US Dollar. Always ensure you are looking at the correct chart.
2. The Direction (Action): BUY This tells you what to do.
-
BUY (Long): You expect the price to go up.
-
SELL (Short): You expect the price to go down.
3. The Entry Price: @ 1.0850 This is the specific price level where you should enter the market.
-
Note: If the current market price is very close to this number, you enter immediately (Market Execution). If the price is far away, you might set a "Pending Order" to catch it when it arrives.
4. SL (Stop Loss): 1.0820 This is your safety net. The Stop Loss is an automatic order to close the trade if the market moves against you. In this example, if the price drops to 1.0820, the trade closes to prevent further loss. Never trade without this.
5. TP (Take Profit): 1.0900 This is your target. When the price hits 1.0900, the system automatically closes the trade and locks in your profit.
"Active" vs. "Pending" Signals
Not all signals are meant to be executed the second you receive them. Understanding the status is key (something you might see in a signal dashboard):
-
Active / Market Execution: "Do it now." The market price is currently at the entry point.
-
Limit / Pending Order: "Wait for it." The analyst believes the price will hit a specific level (e.g., bounce off a support line) before moving in the desired direction. You set the order, and the broker executes it only if the price hits that level.
-
Expired / Closed: The opportunity has passed. Never chase a signal that was sent hours ago if the price has already moved significantly.
How to Use a Signal Step-by-Step
Here is the workflow of a smart trader using a signal service:
-
Receive the Alert: You get a notification (via App, Email, or Dashboard) with the details.
-
Verify the Price: Open your trading platform (like MT4 or MT5). Check if the current price is still close to the suggested Entry Price.
-
Calculate Risk: Before placing the trade, decide your lot size. A good rule of thumb is never to risk more than 1-2% of your account on a single signal.
-
Place the Orders:
-
Select the Pair.
-
Select Buy or Sell.
-
Crucial: Type in the Stop Loss and Take Profit numbers before or immediately after clicking the button.
-
-
Walk Away: Once the trade is set with an SL and TP, let the market do its thing. Avoid the temptation to micromanage the trade.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best signals, traders can lose money if they aren't careful. Here are the "human errors" to watch out for:
-
FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out): Entering a trade after the price has already moved halfway to the Take Profit. If you missed the entry, let it go. There will be another signal tomorrow.
-
Ignoring the Stop Loss: Thinking "it will come back" and removing the Stop Loss is the fastest way to blow an account.
-
Over-Leveraging: Just because a signal has a high success rate doesn't mean you should bet the house. Position sizing is more important than the signal itself.
Conclusion
Forex signals are powerful tools that allow you to leverage the expertise of professional analysts. They save time and reduce the emotional stress of trading. However, knowing how to read them correctly and executing them with discipline is what separates profitable traders from the rest.
Ready to start? Head over to the Signals Dashboard to view today's active opportunities and practice reading the entry and exit points on your demo account first!